What is Gluten Sensitivity?
Gluten sensitivity is a state in which a person has negative reactions to the presence of gluten in their diet. It can take multiple different forms as something that it can be complex as it is related to multiple different autoimmune conditions. Gluten sensitivity has been described as “one of the most frequent lifelong conditions in both the United States and Europe.”1 It can have multiple different manifestations for the person who is suffering from it, and they do not always directly react to foods in a way that clues them in that gluten may be a problem for them.

Gluten-sensitivity is associated with an increased risk of developing autoimmune disease, the third largest reason for mortality and morbidity in the industrialized world. The risk of developing the autoimmune condition in gluten-sensitive enteropathy patients is ten times higher than in the general population. Because of this, the burden that gluten sensitivity places on society cannot be overstated. These people may benefit from early treatment and a higher quality of life when the issue is detected earlier.
A systemic autoimmune condition known as gluten reactivity has many different symptoms. Celiac disease (CD), also known as gluten-sensitive enteropathy, is just one of several potential indications of gluten sensitivity.
Celiac Disease
The most severe problem concerning gluten is Celiac Disease (CD), which is an auto-immune disease of the gut that is exacerbated by the presence of gluten. Celiac disease affects approximately 1 in 133 people, but most have not been diagnosed. The digestive system of someone with celiac disease is attacked by antibodies which can cause microscopic damage to finger-like projection in the small intestine called villi. If the person is not diagnosed with celiac disease and if not treated for the condition, they may develop complications such as malnutrition, osteoporosis, infertility, skin conditions, neurological disorders and even cancer. Celiac Disease is a condition commonly known in the medical community and has been for some time. Celiac disease receives the lion’s share of emphasis, to the point that other indications of the condition are often ignored.
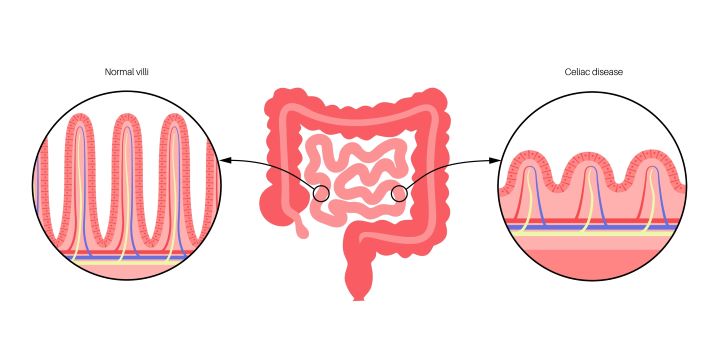
Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity
People can also have sensitivities to gluten but not have Celiac Disease. Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity 2,3, gluten sensitivity and gluten intolerance are typically used interchangeably, and all describe a person that has reactions to gluten without having the intestinal damage seen in Celiac Disease. Gluten intolerance is unlike lactose intolerance in that the problem is not solved by giving a supplement to help digest gluten. Lactose intolerance is caused by the inability to digest the lactose sugar molecule and giving the person an enzyme called lactase can allow the person to digest milk without a problem. Gluten intolerance is not considered a typical allergy, but many use the term “allergy” because of what it conveys to the. People with gluten sensitivity do not react to gluten in the same way some people react to peanuts or shellfish. The typical symptoms of immediate-onset allergic reactions, such as hives, swelling of the face or anaphylaxis, do not happen in gluten sensitive reactions. However, some people do refer to having a “wheat allergy” when referring to their gluten sensitivity to explain to others about the condition.
It is estimated by the Center for Celiac Research at the University of Maryland that approximately six percent of Americans are gluten-sensitive or gluten intolerant. That is about 18 million people that are considered to have Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity (NCGS) and the vast majority of these people do not know that life could be much more comfortable for them. The reactions that gluten-sensitive people have to gluten are very similar to the problems that plague those with celiac disease. Much of the issue can be related to a concept called leaky gut syndrome, where the gut gets inflamed and does not block bad things from getting into your system.
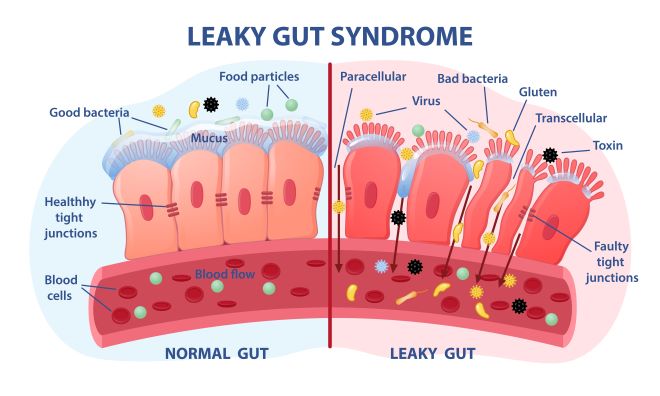
Gluten sensitivity is a controversial topic for some healthcare providers. Some physicians do not recognize the existence of Non-Celiac Gluten Sensitivity, but many have become aware in recent years 4. There is no damage to the villi of the small intestine in someone with gluten intolerance and they believe that the absence of microscopic damage is evidence that there is no problem. On the other hand, the experts in celiac research note that there is a large population of people who are affected by gluten but do not have the structural damage to the gastrointestinal system. Some experts believe that gluten sensitivity is what happens when celiac disease is caught early before the damage to the villi has set in. Some researchers believe that continued exposure to gluten in the diet can eventually push a gluten intolerant person to develop celiac disease, although this has yet to be proven. The incidence of celiac disease and non-celiac gluten sensitivity has increased over time as has other problems such as asthma, immediate onset allergies, ADHD and autism. Currently, researchers are working on the reasons behind such phenomena, but the causes are currently unknown.
Some newer research indicates that more than one molecule may be responsible for the symptoms that are reported by those with NCGS with one being fructan. That being said, a gluten-free diet helps to decrease symptoms because it will lead to a decrease in fructans consumed as well. So for all intents and purposes, a gluten-free diet leads to decreased suffering.
Gluten’s Link to Other Diseases
Gluten exposure can cause disease in several organ systems without showing signs of an enteropathy, including the skin (Psoriatic arthritis, Dermatitis Herpetiformis, Dermatomyositis, Alopecia areata, and Cutaneous vasculitis), muscles (inflammatory myopathies), and the brain (Gluten Ataxia, abnormal neurotransmitter synthesis, Dementia, Schizophrenia, peripheral neuralgias, idiopathic neuropathies).
While very rare, gluten can also be the cause of neurological problems without having problems with the digestive system. Gluten-sensitive idiopathic neuropathy can include problems with movement or balance (ataxia) or numbness and tingling with sensory loss. Some people can have a wheat allergy, where they have a histamine reaction, like those who react to peanuts, shellfish or seasonal allergies like hay fever. Symptoms for these people can be wide-ranging from hives to abdominal pain.

References
- Hadjivassiliou M, Sanders DS, Grünewald RA, et al. Gluten sensitivity: from gut to brain. Lancet Neurol, 2010; 9(3):318-330.
- Leonard MM, Sapone A, Catassi C, Fasano A. Celiac Disease and Nonceliac Gluten Sensitivity: A Review. JAMA. 2017;318(7):647-656
- Fasano A, Sapone A, Zevallos V, Schuppan D. Nonceliac gluten sensitivity. Gastroenterology. 2015;148(6):1195-1204.
- Going Gluten-Free
